VMAC Global Technology Inc., a designer and manufacturer of mobile air compressors and multi-power systems, recently released the results of their annual State of the Mobile Compressed Air Industry Report. The report, which began in 2020, tracks the compressed air industry and its challenges and trends. Each year the report adapts to the changing realities of the industry.
This year, VMAC surveyed 271 participants between December 2023 and March 2024, who answered an average of 31 questions for the online survey. Many in the air compressor industry were represented, with 36 percent being owners, 23 percent being operator/mechanics, as well as sales and marketing (eight percent), fleet managers (eight percent) engineering (seven percent), upfitters (six percent), parts (two percent), purchasing (two percent), and other (eight percent).
“Thank you to everyone who contributes to this report; your input is critical to ensuring the teams working at equipment manufacturers are providing solutions that meet industry needs,” says Tod Gilbert, president at VMAC. “As you will see in the report, the past few years have brought uncertainty in the market, making it difficult for businesses to plan. However, the service truck industry continues to provide critical services to power the projects that provide shelter, food, energy, and transportation to our communities. As our industries persevere through the economic, supply chain, and political uncertainties while navigating new technology, we remain united in getting the right tools in the right hands to keep those critical projects and services running.”
What industries do the respondents belong to? Well, 42 percent of respondents are in equipment repair, 40 percent in construction, 32 percent in agriculture, 21 percent in each of transportation, service truck upfitting, and oil and gas, as well as mobile tire service (17 percent), landscaping (17 percent), municipal infrastructure (16 percent), forestry (15 percent), mining (15 percent), utilities infrastructure (14 percent), and other (15 percent).

VEHICLES AND FLEETS
Would it surprise you to hear that 75 percent of those surveyed said that their service truck fleet consists of one to five trucks? Well, that was an increase of seven percent over 2023. With another 14 percent having 6 to 25 trucks, five percent having over 100 trucks, three percent having 26 to 99 trucks, and three percent having no trucks.
With the rise in truck fleets, the use of service vans is on the decline. As 40 percent of respondents said they have service vans in their fleet (down from 47 percent last year). Of those, 31 percent have 1 to 5 vans, seven percent have 6 to 25 vans, one percent have 26 to 99 vans, and one percent have over 100 vans. On the flip side, 60 percent said they have zero service vans in their fleet, an increase of six percent from last year. Those who are using vans currently, expect to have more in the future (47 percent), but some anticipate a decline (two percent).

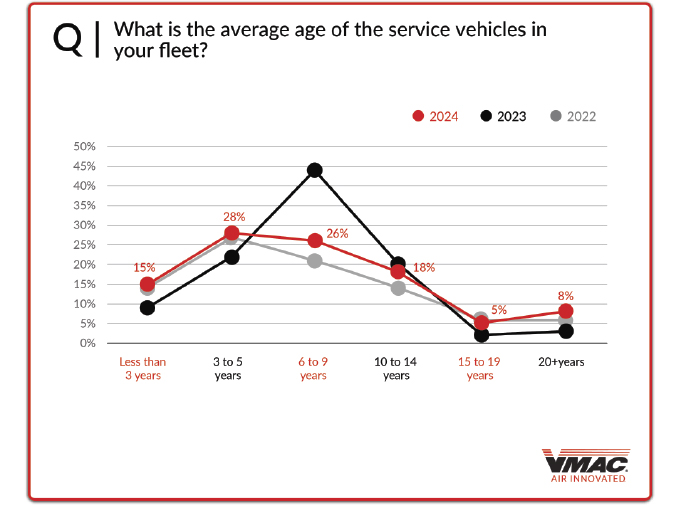
A big aspect of fleet management is how long companies keep their service vehicles in operation. As maintenance costs begin to increase, the older the vehicle, and the overall total cost of ownership becomes important. Overall 69 percent of those surveyed said that the average age of their service vehicles is under 10 years old (15 percent under three years old, 28 percent three to five years old, 26 percent six to nine years old). It is important to point out that 86 percent of respondents who have six or more vehicles, have an average age of nine years or newer. Another 18 percent have vehicles that average 10 to 14 years old.
The remaining 13 percent of respondents indicate that they have vehicles that average over 15 years old (five percent 15 to 19 years old, eight percent over 20 years old). Therefore, those who are most likely to have vehicles in this age group are those who operated one to five service trucks, and in turn do not replace their trucks on a regular basis.
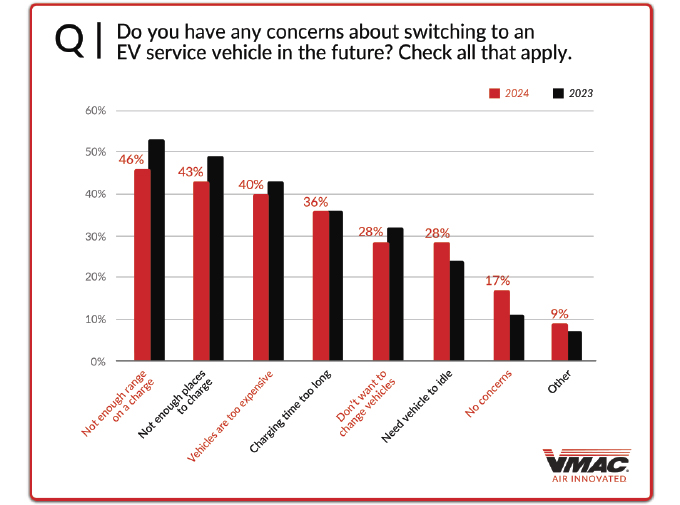
Over the past few years, many OEMs have been introducing electric vehicle options to their fleets. When the question, “do you have any concerns about switching to an EV service vehicle in the future?” was posed to respondents, they indicated that while the number who still have concerns is decreasing (17 percent had no concerns, down from 11 percent in 2023), many still hesitate to make the switch.
What concerns do they have? Not enough range per charge (46 percent) led the way, followed by not enough places to charge (43 percent), too expensive (40 percent), charge time too long (36 percent), do not want to change vehicles (28 percent), need vehicle to idle (17 percent), and other (nine percent).
EQUIPMENT AND AIR COMPRESSORS
Moving over to the equipment that is used on the vans and trucks, unsurprisingly, the most important piece of equipment for respondents was an air compressor (52 percent). This was followed by a crane (13 percent), welder (11 percent), generator (eight percent), and other (16 percent).
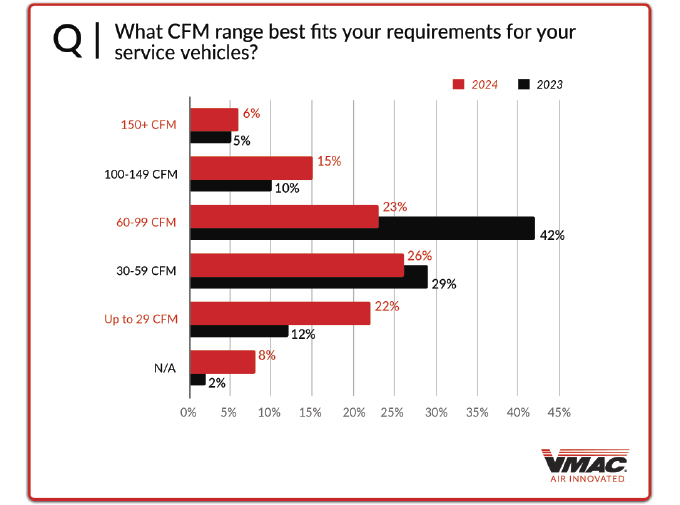
Looking at the air compressors in more detail, this is where opinions diverge, with numbers being much closer together. When asked “what CFM range best fits your requirements for your service vehicles?” The top answer was 30-59 CFM (26 percent), followed by 60-99 CFM (23 percent), up to 29 CFM (22 percent), 100-149 CFM (15 percent), over 150 CFM (six percent), and N/A (eight percent).
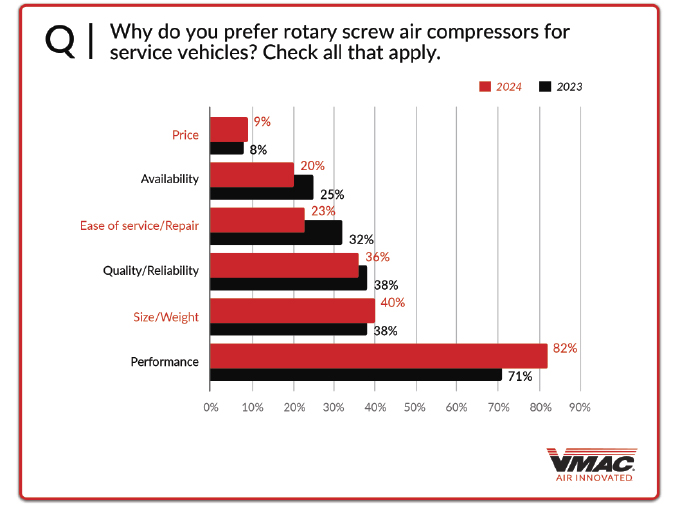
Also, most respondents prefer to use rotary screw air compressors (75 percent) over a reciprocating air compressor (25 percent) for their service vehicles. When asked why they prefer a rotary screw air compressor, the top answer was performance (82 percent), others liked the size/weight (40 percent), quality/reliability (36 percent), ease of service/repair (23 percent), availability (20 percent), and price (nine percent). On the flipside, those who preferred a reciprocating air compressor, did so because of ease of service/repair (56 percent), followed by price (49 percent), availability (47 percent), performance (22 percent), size/weight (18 percent), and quality/reliability (16 percent).
“Comparing Summit Truck Bodies’ data with the insights from VMAC’s 2024 survey results, we’ve observed some compelling trends. Notably, 58 percent of Summit customers spec’ing out a service or lube truck request to include an air compressor, and 73 percent of these requests are for a rotary screw compressor rather than a reciprocating compressor,” says Sondra Kirby, marketing manager at Summit Truck Equipment.
“Looking at CFM, 40 CFM rotary screw air compressors are the most popular model, accounting for 81 percent of all air compressor sales. Our customers consistently choose rotary screw air compressors for their reliability, smaller size, and lighter weight compared to other above-deck air compressors. These preferences align with VMAC’s survey findings, highlighting the market’s ongoing demand for efficient, high-performance air compressor solutions.”
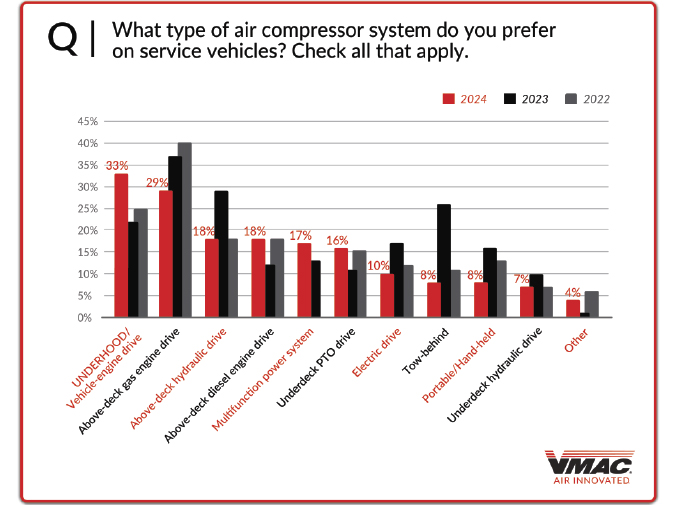
One last question asked under the air compressor section was: “what type of air compressor system do you prefer on service vehicles?” With the top three answers being Underhood/vehicle-engine drive (33 percent), above-deck gas engine drive (29 percent), and above-deck hydraulic drive (18 percent).
IMPACT ON BUSINESS
Numerous factors have been impacting the industry over the last year, from ongoing supply chain issues that came to a head during the COVID-19 pandemic, to rising interest rates, and finally to labor challenges.
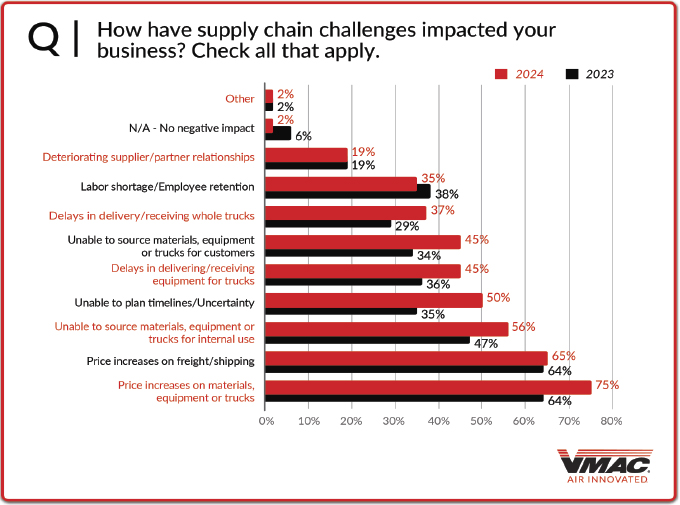
Looking at supply chain challenges, 62 percent of respondents said that their business has been negatively impacted. Of those negatively impacted, 75 percent said that the main reason was price increases on materials/equipment/trucks, followed by price increases on freight/shipping (65 percent), unable to source materials/equipment/trucks for internal use (56 percent), unable to plan timelines/uncertainty (50 percent), and delays in delivering/receiving equipment for trucks (45 percent). It is interesting to note, that almost every category grew from 2023 to 2024.
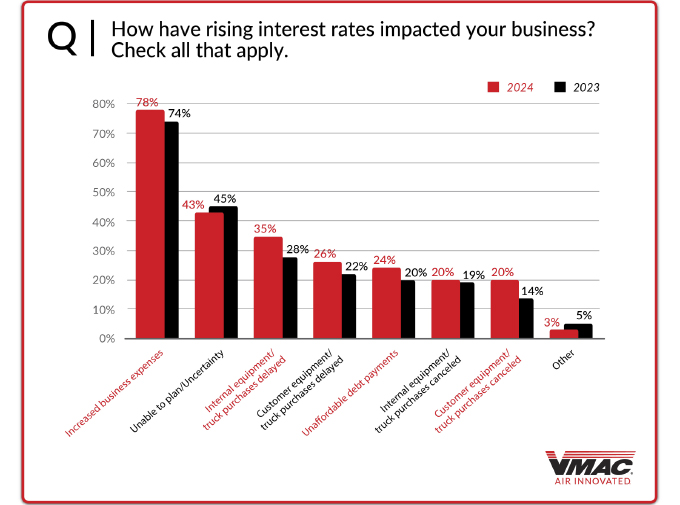
Interest rates have been climbing since the pandemic began, however, they may be on their way down soon. Most businesses (54 percent) reported that they have been negatively affected by rising interest rates. Breaking this down further, those negatively impacted, cited increasing business expenses (78 percent) as the main cause, with unable to plan/uncertainty (43 percent), internal equipment/truck purchases being delayed (35 percent), customer equipment/truck purchases delayed (26 percent), and unaffordable debt payments (24 percent) rounding out the top five.
For the 2024 addition of the survey, a new question was added, asking “in what ways have labor challenges impacted your business?” Unsurprisingly, 72 percent of respondents cited labor shortages/not being able to fill vacancies as the main problem. This has been seen across a number of industries. Employee retention (63 percent), inflation/rising wages (54 percent), recruitment (48 percent), increased hours/burnout (42 percent), low employee morale (41 percent), increased employee absences (37 percent), and other (three percent), were all seen as challenges facing businesses.
“Similar to last year, inflation affected by labor, cost of living, and higher-cost materials resulted in higher COGs. We are seeing material availability improvements in some commodities. However, more specialized equipment manufacturers are extending lead times and implementing allocations,” says Yolande Freed Dunbavin, supply chain manager, VMAC. “In an effort to reduce the impact of increased material costs, proactive businesses are actively seeking alternative supply chain strategies and technologies. This approach is designed to ensure operations remain resilient and adaptable in the face of changing market conditions.”
LOOKING TO THE FUTURE
What does the future hold for businesses? Respondents were cautiously optimistic, with 45 percent believing that business conditions for the next 12 months will remain the same, and 29 percent saying they think they will get better. However, just over a quarter (26 percent) look at the next 12 months as being worse.
“Over the last year and heading into 2024, central banks in North America appeared poised to initiate interest rate cuts. Now, inflation is on a good downward path, though growth in interest rate-sensitive parts of the economy remains strong, creating some risk,” says Brent Johnston, CEO, VMAC. “Generally, North American economies are experiencing strong employment growth, strong wage growth, and, in some pockets, record population growth. A focused and strategic approach to business and operations will mute any continued volatility in labor, materials, or other investments.”
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mario Cywinski is the editor of Modern WorkTruck Solutions and has worked in the automotive industry for 20 years, both as an automotive journalist and working for a local dealership. He is a member of the Automobile Journalist Association of Canada and has been a judge for the Canadian Truck King Challenge. He can be reached at mario@mwsmag.com.




